|
|
Cmarc |
AeroLogic
Personal Simulation Works |
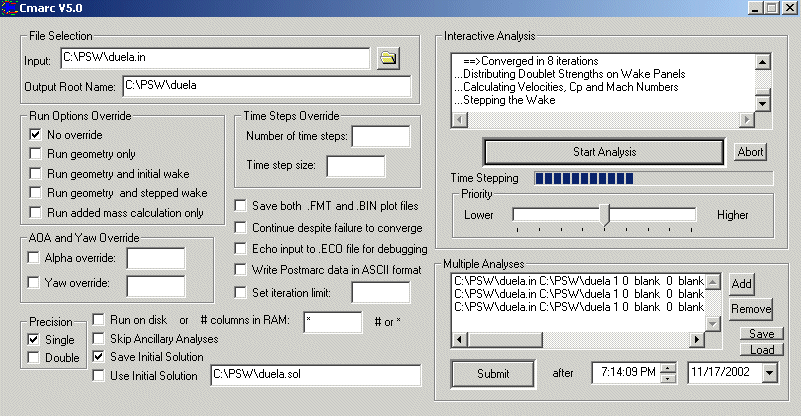
| Cmarc is a inviscid fluid flow analysis program of the type known as a low-order panel method. It is an enhanced version of NASA's Pmarc-12, which is in turn a descendant of an early version of Analytical Methods' VSAERO. Pmarc-12 and VSAERO took different evolutionary paths, but their common ancestry is apparent in the similarity between their input file formats and the results that they produce. Low-order panel methods, in which the calculated coefficient of pressure for each panel is applied uniformly over the entire panel, have been shown to provide virtually the same level of accuracy as higher-order methods, in which pressure gradients are calculated within panels, so long as the meshing of the model is sufficiently dense, particularly in areas of rapidly changing pressure coefficient. On modern desktop and laptop computers, dense meshes of 5,000 or more panels for a half-model can be analyzed in seconds. Although the basic analysis is inviscid, a subsequent boundary-layer analysis may be performed along individual streamlines or over the entire surface. Provided that flow is attached and that large areas of crossflow do not appear, the boundary layer analysis is quite accurate. Only the frictional and lift-induced components of drag can be computed, however, unless the user chooses to use Cmarc's nonlinear option, which incorporates boundary-layer displacement in the iterated solution. While an inviscid analysis is inherently unable to calculate pressure or "form" drag, iterating over the boundary layer allows Cmarc to predict pressure drag with good accuracy so long as large areas of separated flow are not present.. Cmarc and Pmarc-12 input files are mutually compatible. Cmarc's output formats are a superset of Pmarc-12's; Cmarc adds several files whose purpose is to communicate output data to Postmarc. Postmarc incorporates a number of Cmarc procedures, particularly those related to the boundary layer analysis, in order to permit interactive generation of on- and off-body streamlines and of pressure and velocity maps of the free stream. With Cmarc and Postmarc, it is not necessary to re-run the entire analysis each time new streamlines or velocity scans are desired. Cmarc's program screen (below) allows the user to alter a number of parameters and run conditions without editing the input file. In this it resembles the "Analysis" screen in Digital Wind Tunnel (DWT). Batch processes can be scheduled to occur at any future date and time, and batch files can be saved and reused. Memory detection and management work the same as in Digital Wing Tunnel. Cmarc, which is written in ANSI C, can also be delivered to customers in command-line form, either as a DOS executable or as UNIX-compatible source code with a makefile. Source code is provided at AeroLogic's discretion, and may be modified by the user, but not redistributed.
| |
| | |
 Copyright 2018, AeroLogic |
This page designed and maintained by Dave Web Works |